Experimental Archaeology
Probable Measure Estimating Tool Employed by the Aeneolithic Potters
The Theory of the Archaeological Raft: Motivation, Method, and Madness in Experimental Archaeology
Between 1947 and 2006, nearly forty expeditions set out in recreated maritime drift vessels to demonstrate hypotheses with varying levels of relevance to archaeology and cultural diffusion. This paper divides the motivations of these expeditions into four major categories...
Contribution to the Medieval Building Technology Based on the Reconstruction of a Rounded Church
This article presents the experimental archaeological project to build a medieval rotunda reconstruction using rough stone building technology. Here, a medieval rotunda reconstruction is presented by contemporary building technology...
"But if you don't get any IRON..." Towards an Effective Method for Small Iron Smelting Furnaces
Building and operating a small bloomery iron furnace is certainly a wonderful public demonstration for any museum or living history site. It is however a complex technical process, with many individual factors combining for success. Over the last decade in North America, small teams of blacksmiths have developed predictable working methods through trial and much error. This direct practical experience can provide some insights into questions that even the best researched theories may not be able to solve.
The Experiment and the Umbrella - 10 Years of Experimental Archaeology
Who are the contributors?
First of all it is interesting to see who the participants in the discussion of the archaeological experiment are. Certainly, the articles I have selected and read are only representative of a fraction of the contributions, but it is clear that it is primarily those who work with experimental archaeology in their research. Participants from outside this group are rare. This is regrettable as the archaeological experiment is an important method in archaeological research in general.
Ancient Wood, Woodworking and Wooden Houses
1987 ESF Proceedings
The 1980s was the beginning of a boom in the construction of archaeologically inspired buildings inside and outside archaeological open-air museums.
***
This article introduces a record on the management and use of prehistoric woodland gained from the research of the Somerset Levels...
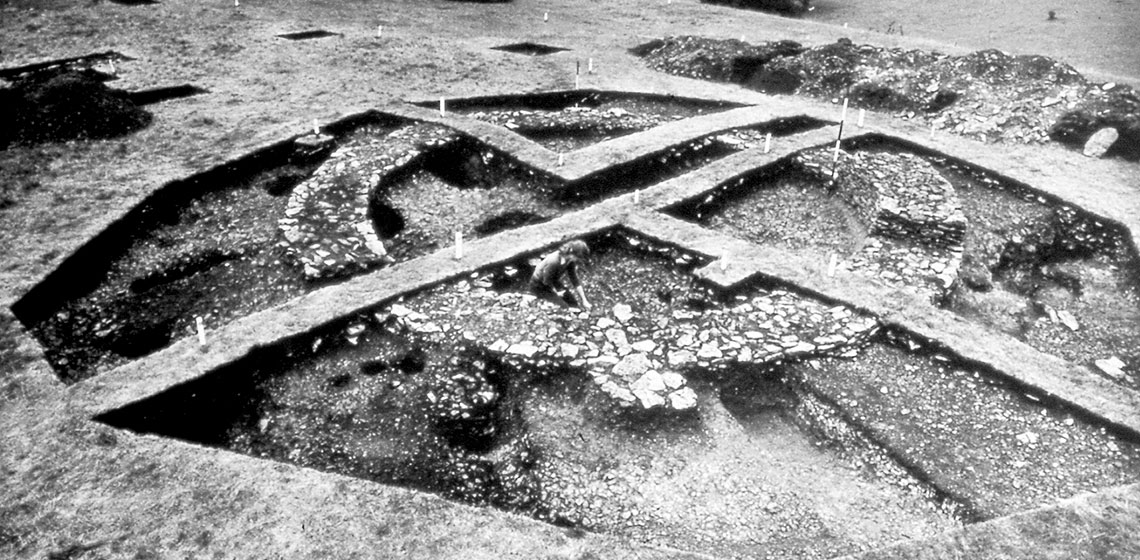
The Scientific Basis for the Reconstruction of Prehistoric and Protohistoric Houses
In 1966 just outside the boundary of a hill fort known as Kemerton Camp on top of Bredon Hill (Hencken 1939) in Worcestershire a small roundhouse was reconstructed, based upon the excavations carried out at Glastonbury Lake Village some fifty years before (Reynolds 1967a, Bullied and Grey 1911). A group of students under the guidance of Mr. Philip Barker of Birmingham University, carrying out a routine site visit, were deeply impressed to come across the three dimensional reality of something which had been previously discussed in vacuo.
Publishing Archaeological Experiments: a Quick Guide for the Uninitiated
How to publish Experimental Archaeology?
*** As an academic archaeologist engaged in experimental archaeology, I frequently find myself frustrated by three different types of archaeological publication...
For the Reader’s Sake: Publishing Experimental Archaeology
How to publish Experimental Archaeology?
*** Archaeological experiments should be presented as concisely as possible, with a clear explanation of the reason (or justification) for the experiment and the significance (and limitations) of the results...