skin or leather
Adventures in Woad: Woad Dyeing in the Ancient, Medieval, and Modern Worlds
Publication Date
In this article, we explored woad and its uses as a dye on both cloth and skin. Using experimental methods, we constructed woad vats using recipes and techniques from modern, early modern, and medieval times to better understand how dyeing with this key dye material of the ancient and medieval worlds functioned. We also experimented with dyeing techniques on skin to better understand the passage in Caesar's Gallic War which references Gauls with blue-dyed skin...
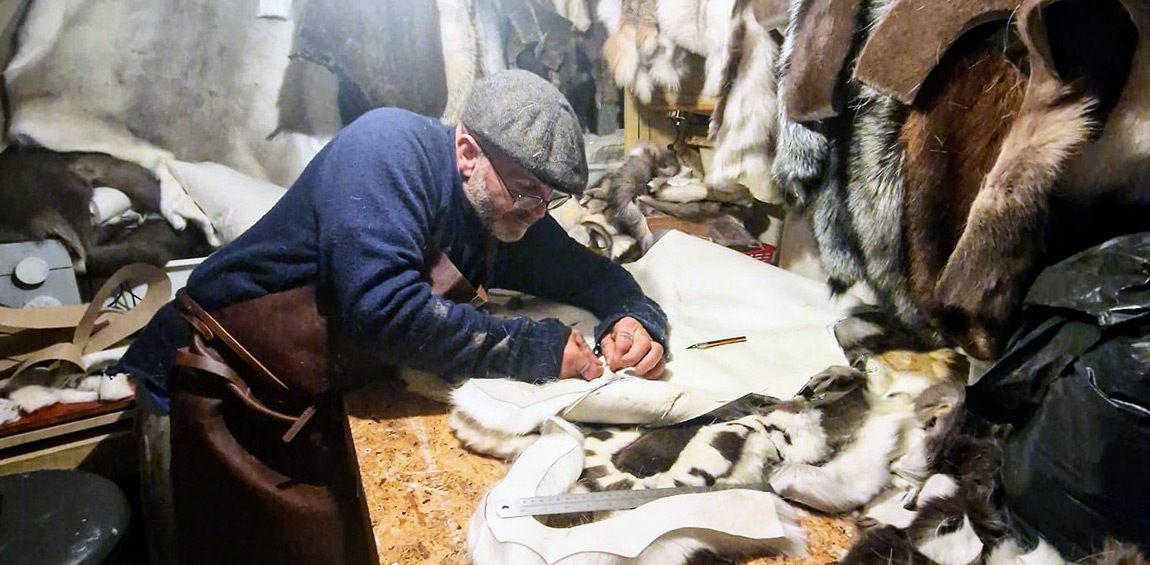
Interview: Richard Rees, a professional furrier with over 30 years of experience
Publication Date
We are talking to Richard Rees, a professional furrier with over 30 years of experience in the profession. He has undertaken an unprecedented project - creating the fifth Qingailisaq parka. The parka is famous for being so difficult to make.
Neanderthals in the Rain: Assessing Neanderthals' Strategies to Survive Wet and Cold Environments through an Experimental Analysis
Publication Date
Neanderthals' adaptations to cold climates have been extensively debated, however, limited attention has been given to their survival in cold and wet environments. These conditions increase the dangers of cold-induced injuries such as frostbite or hypothermia, as wet clothing loses its insulative capacities. This research explores whether and how Neanderthals faced such changes and their implications on activities and behaviours...
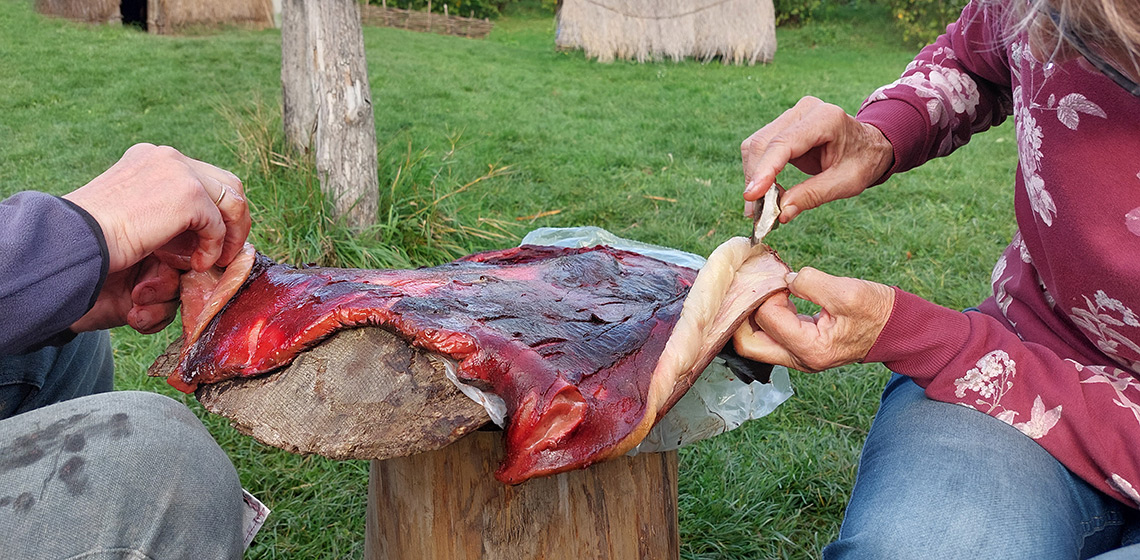
Scraping Seal Skins with Mineral Additives
Publication Date
Neolithic scrapers from the Vlaardingen Culture (3400-2500 BC) display a variety of hide-working traces, amongst which traces interpreted as being the result of contact with dry hide. It has been suggested that, potentially, some of these implements were used to scrape fatty hides with mineral additives. Therefore, a series of experiments...
Book Review: Natural Leather Tanning by Markus Klek
Publication Date
Writing a book on a primitive technology in today’s fast-paced society, fueled by the internet and instant gratification by observing a skill through video, is a risky endeavor. Adding to this risk is the fact that there are many books about brain tanning already on the market. ..
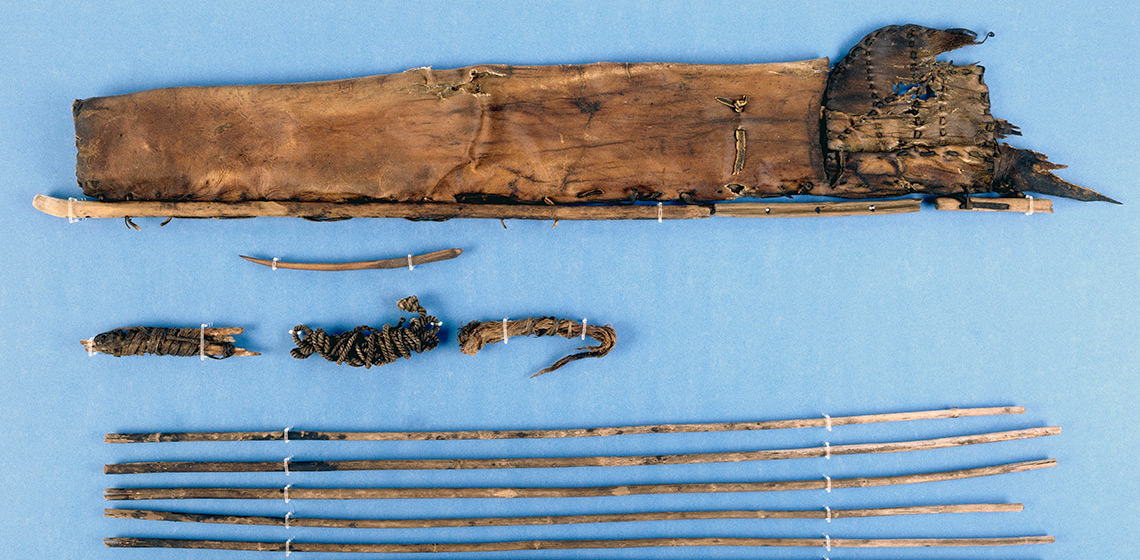
The Arrow Quiver of the Iceman Reconstruction Attempts and the Special Significance of the Fur Material
Publication Date
In 1991, the sensational discovery of a male mummy, thawing from the ice, was made on the Tisenjoch in the Ötztal Alps, near the Austrian-Italian border. The deceased man lived about 5300 years ago at the end of the Neolithic Age and is commonly known as Ötzi in German-speaking countries. The site also contained many well-preserved accompanying items and equipment...
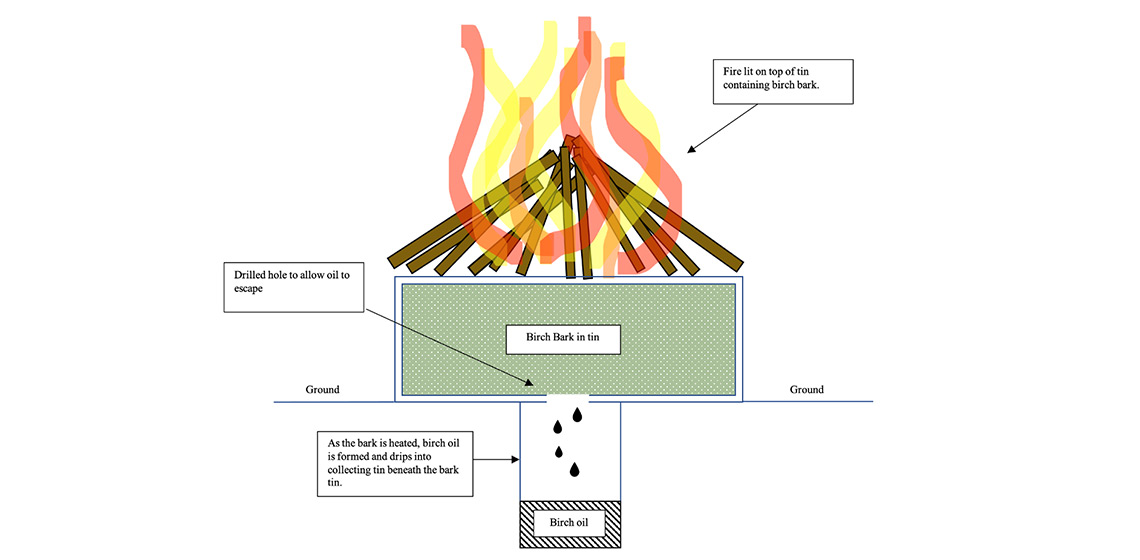
Birch Bark Glue and its Potential Use in Neanderthal Clothing: A Pilot Study
Publication Date
Evidence that Neanderthals had mastered the production of birch bark tar as an adhesive has generated important and timely debate concerning behavioural complexity. Increased resolution of the data on palaeo-climatic conditions has also brought into sharp focus the need for hominins living in high latitudes to possess complex cultural mechanisms to deal with cold environments...
Book Review: Determining Prehistoric Skin Processing Technologies by Theresa Emmerich Kamper
Publication Date
This volume on prehistoric tanning technology is the revised and expanded version of the dissertation submitted to Exeter University in 2015. It is noteworthy in that it places experiment at the heart of the entire research programme, thereby radically changing the perspective from which archaeological and ethnographic artefacts might be approached...
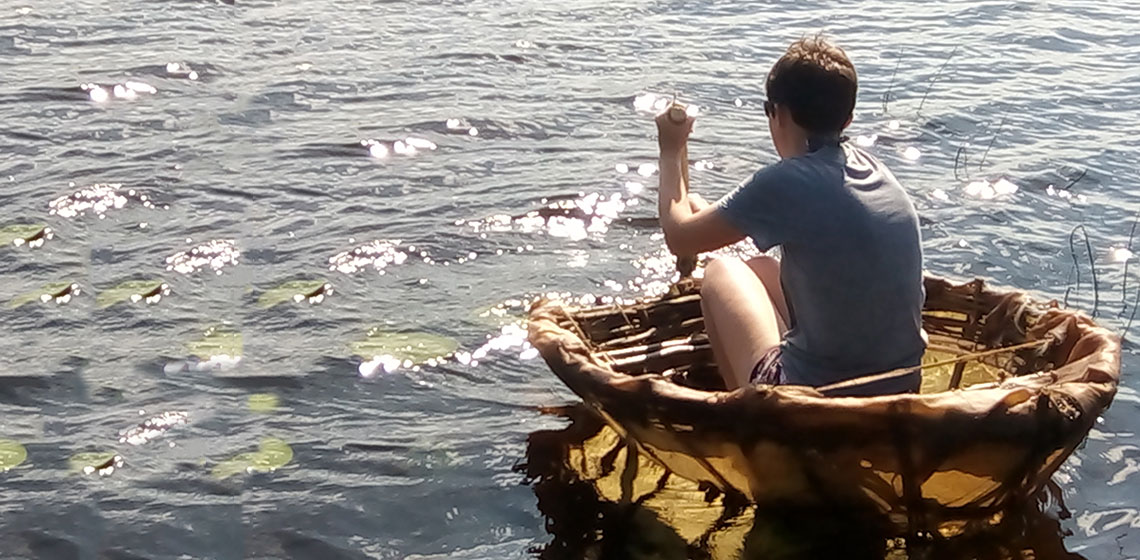
The Construction of a Skin-on-Frame Coracle at Kierikki Stone Age Centre
Publication Date
In July 2018 a group of students from the UK participating in the Placements in Environmental, Archaeological and Traditional Skills (PEATS) Erasmus + Work Placement, attended the Kierikki Stone Age Centre, Pahkalantie, Finland. During the week previous to this experiment, the same group of students had built a skin-on-frame canoe, so the decision was taken to build an alternative lightweight craft...
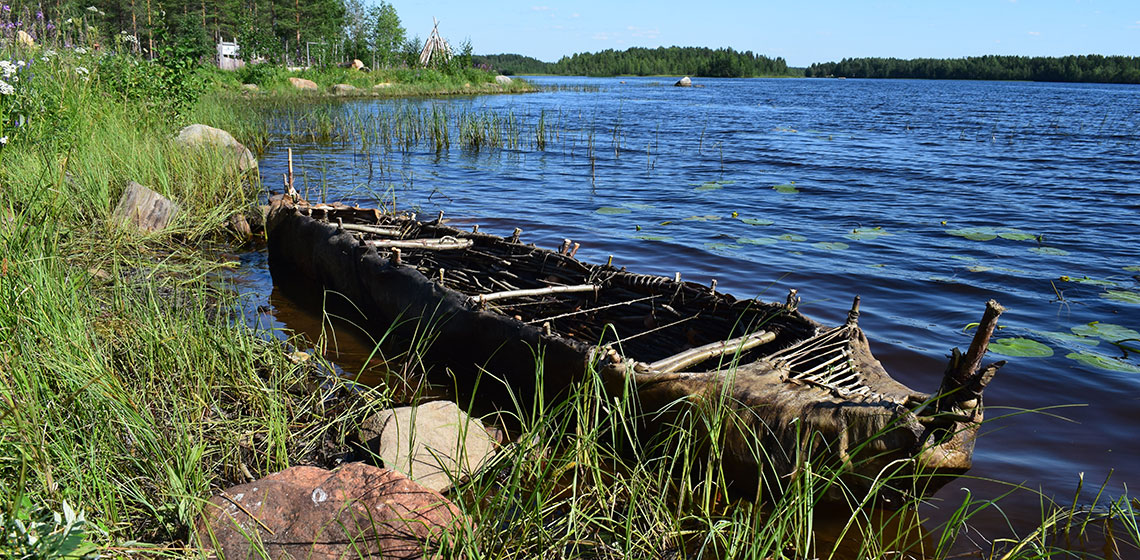
The Construction of a Skin-on-Frame Canoe at Kierikki Stone Age Centre, Finland, as a Medium for Group Training in Ancient Skills and Experiential Learning
Publication Date
In July 2018 a group of students from the UK participating in the Placements in Environmental, Archaeological and Traditional Skills (PEATS) Erasmus + Work Placement, attended the Kierikki Stone Age Centre, Pahkalantie, Finland. Part of that training included experimental / experiential projects that were coordinated by Dr. Peter Groom of the Mesolithic Resource Group...