The content is published under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Themed Collections:
Reconstruction of Wooden Buildings (ESF)

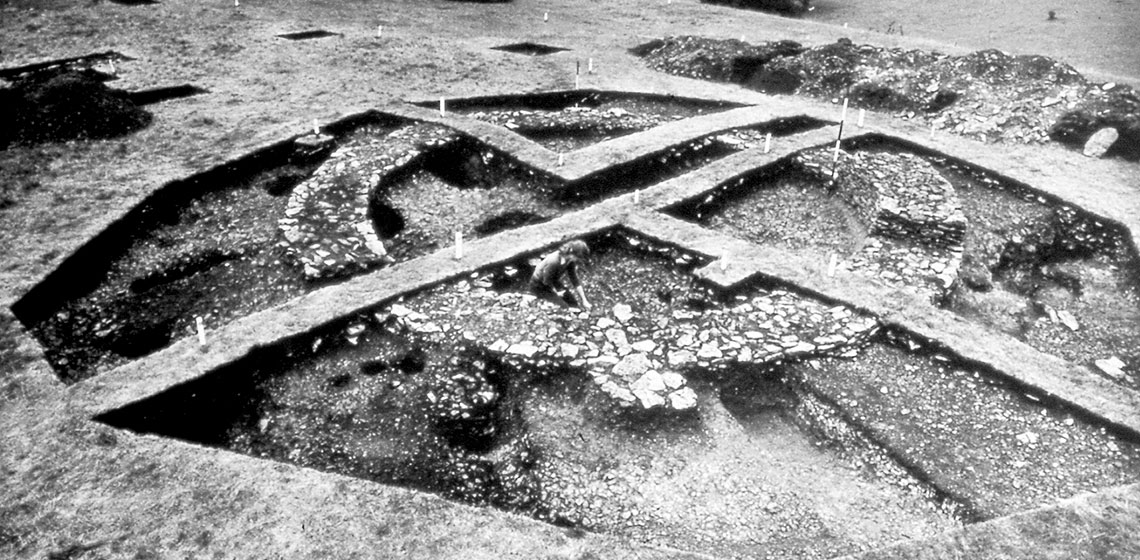
The 1980s were the beginning of the construction of archaeologically inspired buildings inside and outside archaeological open-air museums. 1987, a workshop took place in Århus, Denmark with 31 specialists from 13 countries attending. It was organised by the subcommittee on Archaeology of the European Science Foundation (ESF) and was themed: "the reconstruction of wooden buildings from the prehistoric and early historic period".
The 1987 ESF workshop in Århus on the reconstruction of wooden buildings was initiated by professor H.T. Waterbolk from Groningen, Netherlands and professor O. Olsen from Copenhagen, Denmark. In their proposal to the ESF, they wrote of the problems of constructing at a 1:1 size. Some of the problems addressed are still valid today.
Waterbolk & Olsen described the lack of exchange between those involved as a reason for the workshop: "reconstructions have so far been isolated enterprises...". This is exactly the same reason which started EXARC in 2001 and the EXARC Journal which is also meant to foster a communication and to reach, as Waterbolk and Olsen put it for their workshop: "a joint national or international effort to make optimal use of the new data".
Unfortunately, the proceedings of this workshop were not published. Just a couple of the problems that hindered the manuscript from being published were that one of the editors retiring shortly after and none of the texts were available electronically. In addition, when we rediscovered the manuscript in about 2005, one of the editors, Dr Reynolds, had unfortunately already died.
Of course many of the texts have by now already been published in one form or the other. However, a reasonable amount of the material still deserved to be presented, as the ideas are still valid and haven’t been issued elsewhere. The progress of modern techniques, which at first hindered publication, has now been an advantage as we scanned the texts. The original session organisers, Waterbolk and Olsen have also agreed to us publishing these articles, as long as the original authors agree.
It is with pleasure therefore that we can now offer these "ESF Proceedings". We advise the readers not only to try and view the articles in the light of the 1980s, but to also see their relevance to the present.
Please see also Book Review: Glossary of Prehistoric and Historic Timber Buildings by Lutz Volmer and W. Haio Zimmermann (ed.) - a contribution to this conference.
Featured
Yeavering Reconsidered
1987 ESF Proceedings
The 1980s was the beginning of a boom in the construction of archaeologically inspired buildings inside and outside archaeological open-air museums.
***Brian Hope-Taylor’s report (1977) on his excavations at Yeavering was received with a unanimous fanfare of approval from reviewers...
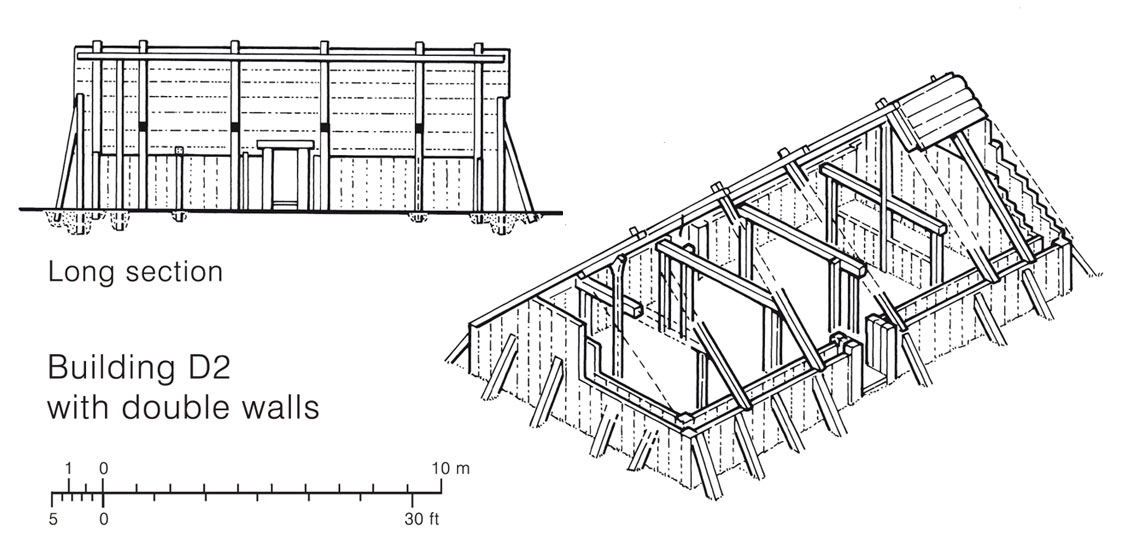
The Reconstruction of the Danubian Neolithic House and the Scientific Importance of Architectural Studies
1987 ESF Proceedings
The 1980s was the beginning of a boom in the construction of archaeologically inspired buildings inside and outside archaeological open-air museums.
***The purpose of this paper was to explore the scientific basis of building reconstructions. The critical issue was to address the problems of reconstruction in order to specify limits within which the reconstruction is of research/educational value and to a set standards which may act as guidelines.
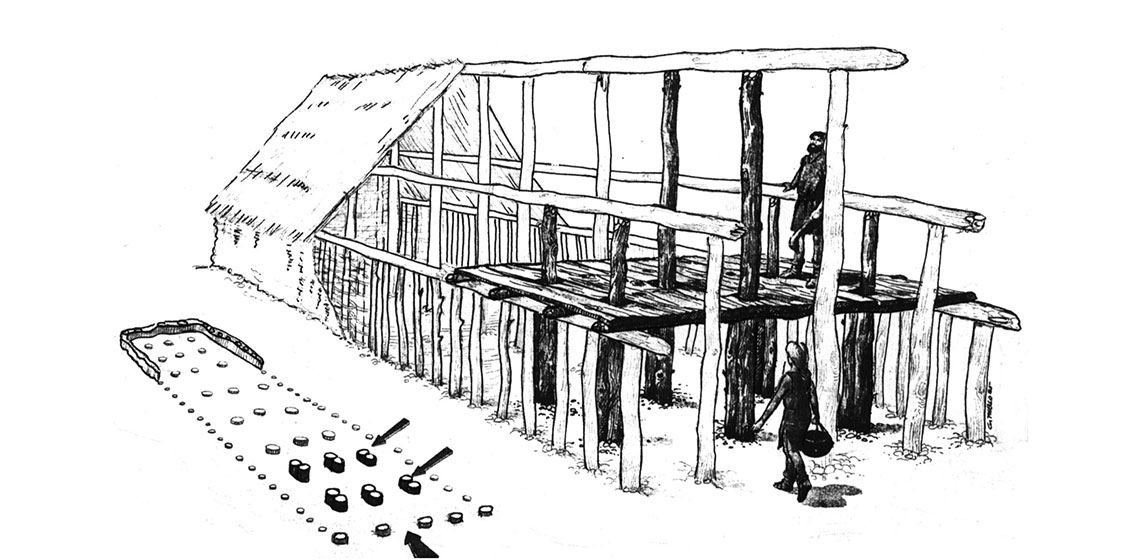
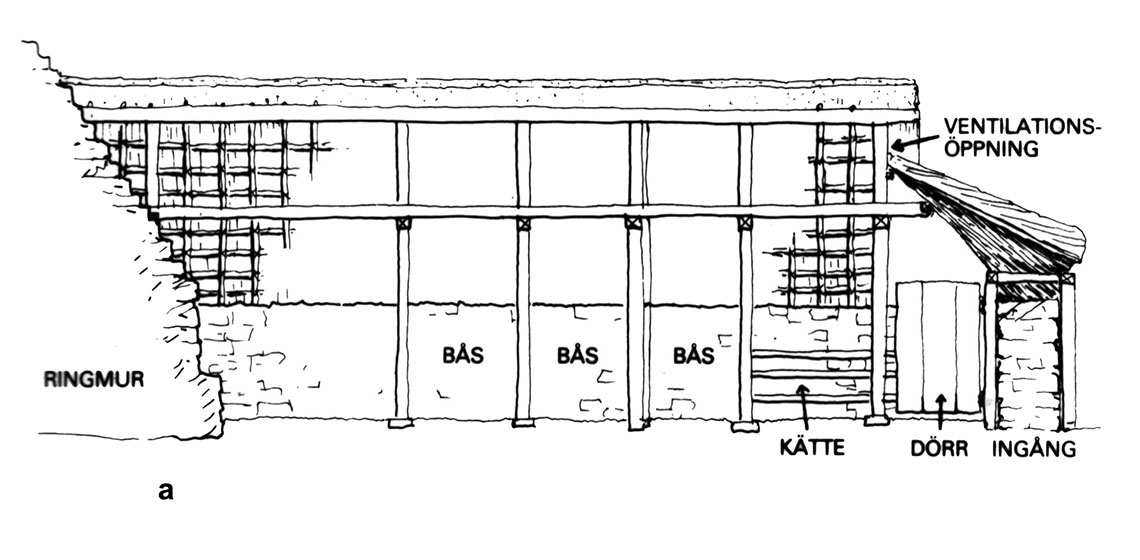
Aspects on Realizing House Reconstructions: a Scandinavian Perspective
1987 ESF Proceedings
The 1980s was the beginning of a boom in the construction of archaeologically inspired buildings inside and outside archaeological open-air museums.
***Experiments are an integrated part of archaeological research, a tool used to analyse and understand archaeological phenomena. It is a method as legitimate and as problematic as so many others. The reconstruction of wooden buildings is a main branch of experimental archaeology.
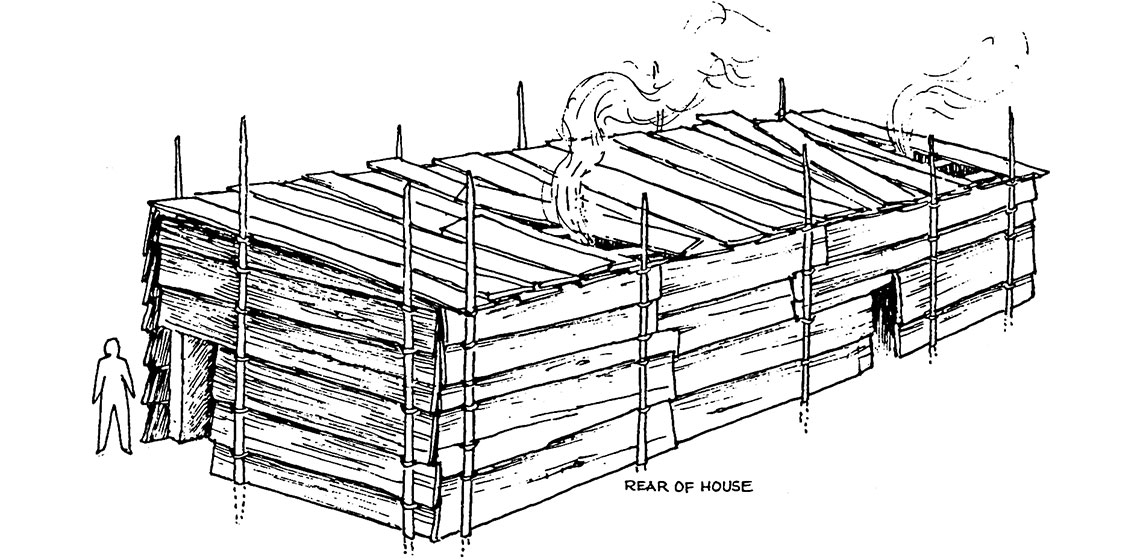
Ancient Wood, Woodworking and Wooden Houses
1987 ESF Proceedings
The 1980s was the beginning of a boom in the construction of archaeologically inspired buildings inside and outside archaeological open-air museums.
***This article introduces a record on the management and use of prehistoric woodland gained from the research of the Somerset Levels...
The Scientific Basis for the Reconstruction of Prehistoric and Protohistoric Houses
1987 ESF Proceedings
The 1980s was the beginning of a boom in the construction of archaeologically inspired buildings inside and outside archaeological open-air museums.
***The purpose of this paper was to explore the scientific basis of building reconstructions. The critical issue was to address the problems of reconstruction in order to specify limits within which the reconstruction is of research/educational value and to a set standards which may act as guidelines.