EXARC Journal - Latest Articles
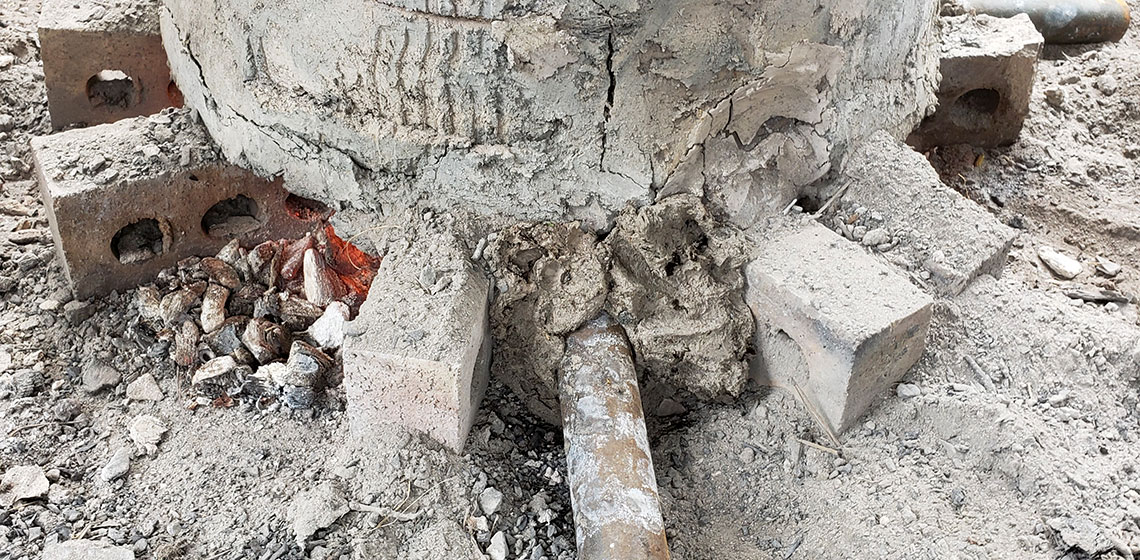
The Mother of All Bead Furnaces: Testing a Hypothesis about a Natural Draft Bead Furnace
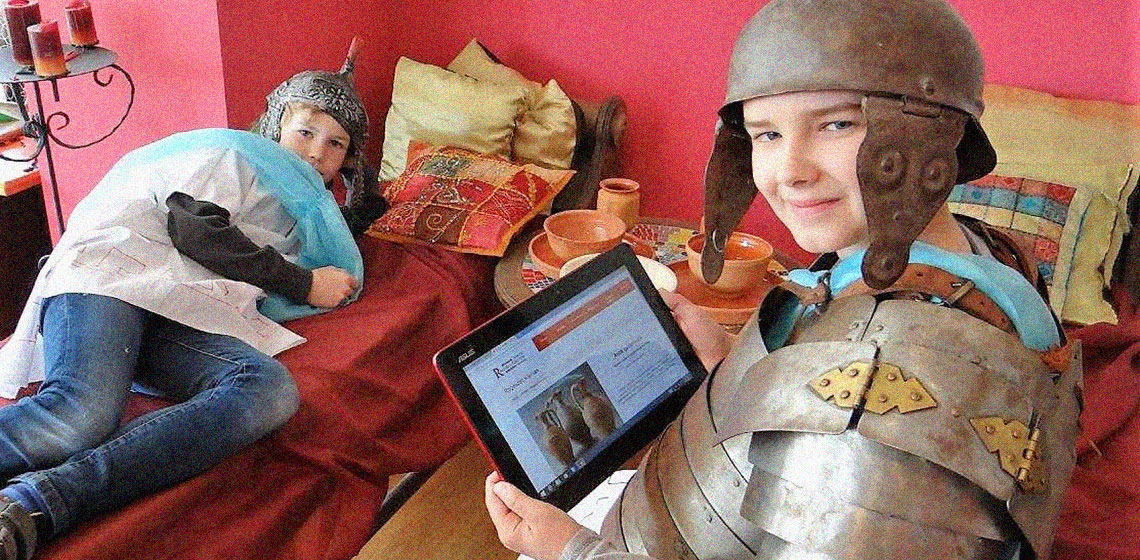
How to Make a Medieval Town Come Alive – the Use of Volunteers in Living History
***For over 25 years The Medieval Centre/Middelaldercentret in Nykøbing F. Denmark has used volunteers to inhabit the reconstructed medieval town of Sundkøbing. To combine the use of volunteers and living history is not easy or something that happens spontaneously. It is hard work and requires patience, strength and firmness, but also...
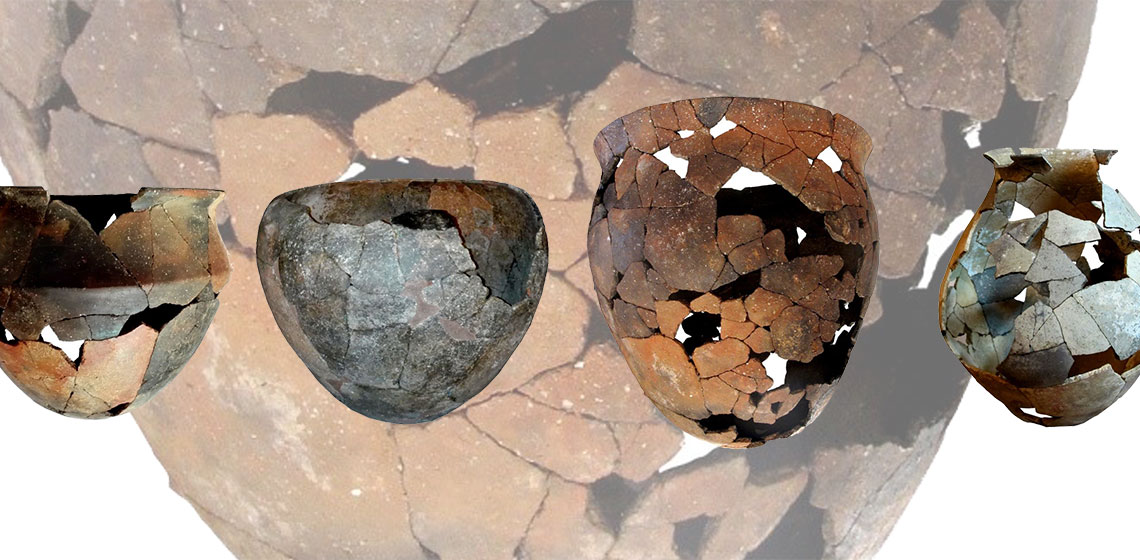
CRAFTER: An Experimental Approach to Fire-Induced Alteration of Pottery Fabrics
Book Review: Experimental Archaeology: from Research to Society, by Isabel Cáceres et al.
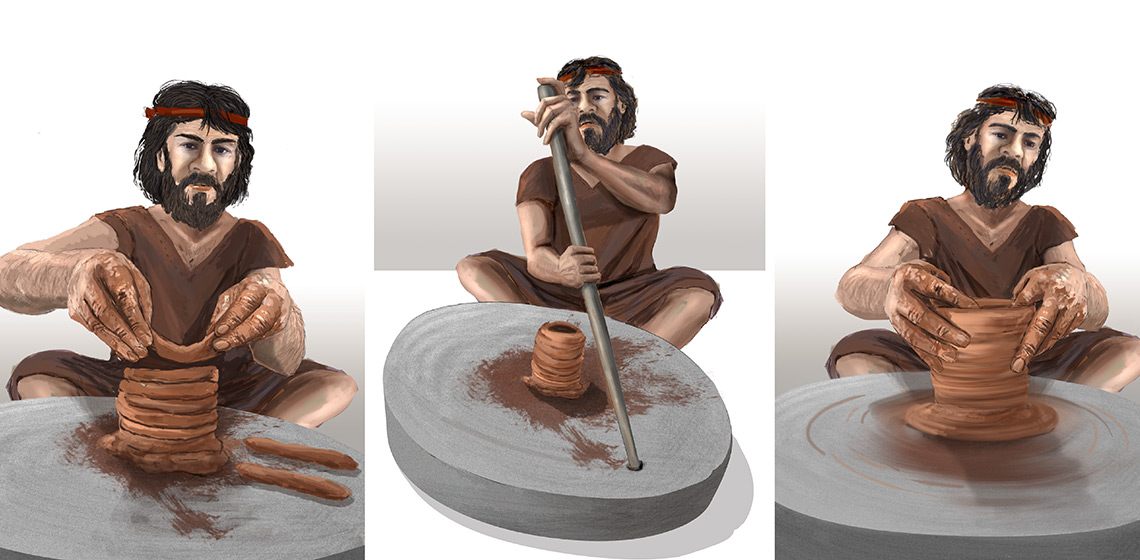
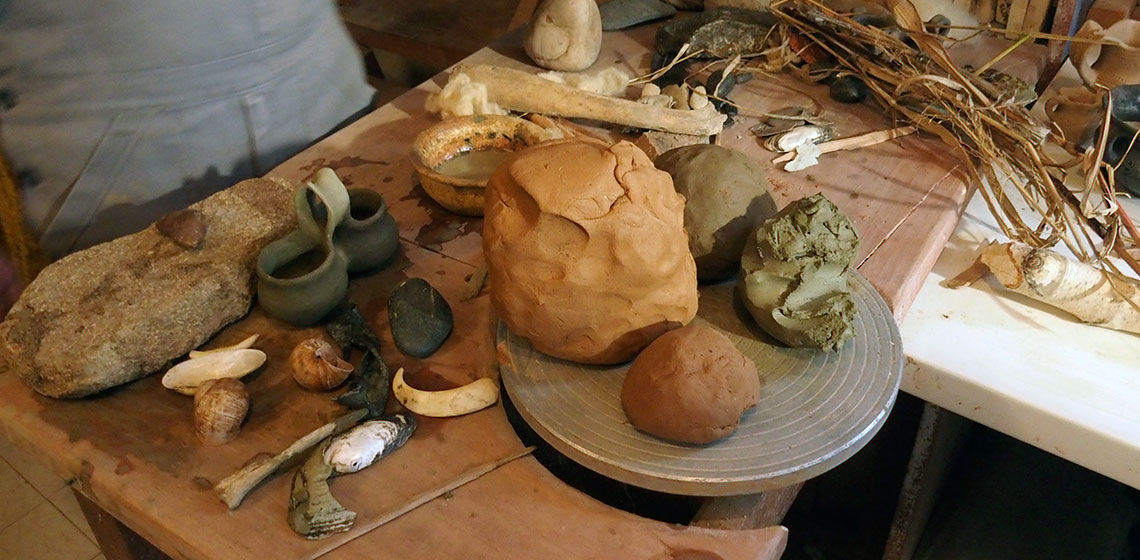
CRAFTER: Re-creating Vatin Pottery 2: an Examination of Clay Quality and its Behaviour
The Bronze Age Vatin culture has been known in archaeology as a cultural phenomenon distinguished by a specific material culture which existed between c. 2200 to 1600 B.C. in the region of the southern part of the Pannonian Plain, and the area along the lower Sava river and south of the Danube river. The Vatin culture followed on from the Early Bronze Age cultures in the region, indicating stabilization in this area after the disintegration of the Aeneolithic Vučedol culture by tribes from the Russian steppe (Garašanin 1979, p. 504; cf.
 The EXARC Journal (since 2004) is the leading Journal for those involved in
The EXARC Journal (since 2004) is the leading Journal for those involved in